Uses and Benefits
It's no secret that vitamins and nutrients are necessary to maintaining a healthy lifestyle. By either adhering to a certain diet, or supplementing with multi-vitamins, many of us aim to ingest those recommended daily doses. Often times people will up the intake of a certain vitamin to either improve the health of certain organs, or prevent possible deterioration. Examples include the prevention of bone disease, increased immunity, improved digestion, detoxifying, and the promotion of healthy vision. But what about hearing loss? Only recently have certain vitamins been linked to the prevention of hearing loss and the overall improvement of existing hearing impairment.
There are many different things that can lead to an individual developing hearing loss. The cause and type of hearing loss will determine the effectiveness of vitamins as a source of relief. Before diving into the different vitamins that can be tied to hearing improvement, one must understand the various types of hearing loss and how certain ones can be prevented.
Types of Hearing Loss
To understand how vitamins can be an effective means for hearing loss relief, it's important to be familiar with the different forms of hearing loss and the associated causes. Currently there are 3 main types of hearing loss- Conductive, Sensorineural and Mixed- all of which can develop in a number of ways and each with a variety of available treatments. Hearing loss, in any form, is something that can result from a condition which exists at birth, or individuals can develop it over time.
Conducive Hearing Loss
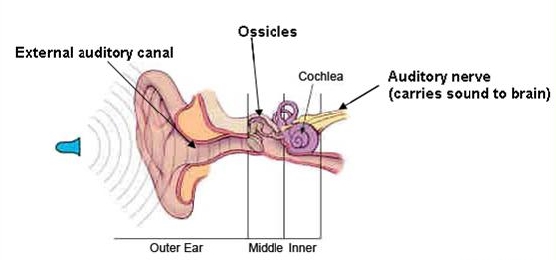
Conductive Hearing Loss refers to any damage to the nerves within the ear canal, the eardrum or the middle ear. Indicative of Conductive Hearing Loss is any instance in which sound is not able to reach the inner ear to be processed by the brain.
There are many possible causes for Conductive Hearing Loss which can include malformation of the ear, ear infection, perforated eardrum, a foreign body within the ear, buildup of fluid or earwax, or poor function of the Eustachian tube. Considered highly treatable, Conductive Hearing loss has a variety of treatment options ranging from surgical procedures to anti-fungal medications, to conventional hearing aids.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
The second type of hearing loss is called Sensorineural Hearing Loss and it occurs when damage has been done to the hair cells within the inner ear. Common causes include noise-induced trauma, head trauma, and benign tumors to genetic predisposition and otoxic drugs (drugs which are used to treat serious illnesses yet can damage the ear). Trauma due to extreme noise trauma is highly preventable and vitamins (along with ear plugs and other forms of protection) can help limit the extend of potential damage.
Vitamins are a great method for increasing immunity within this sensitive organ and can can help reverse damage to a certain extent, but for more extreme cases there are a variety of more intensive treatment options.
Mixed Hearing Loss
Mixed Hearing Loss, as the name would indicate, is when both Conductive and Sensorineural Hearing Loss are present. Causes can include any combination of triggers which result in both damage to the inner and outer ear. When attempting to treat Mixed Hearing Loss, medical professionals will first attend to the damage within the middle and outer ear (Conductive Hearing Damage) to ensure that sound can successfully pass through the eardrum.
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
Though there are a variety of potential triggers for hearing impairment, damage caused by extreme noise is one of the targets when opting to use vitamins for preventing or improving hearing loss. It's important to note that noise-induced hearing loss can result over time from chronic exposure to loud noises, like power tools, loud music, or aircraft noise, or it can also stem from one instance of sudden loud sounds, like an explosion. The damage occurs when the tiny hair cells which process the sound information are exposed to high decibels of sound, and the information therefore does not reach or get registered by the brain.
Ingesting certain vitamins can increase the body's natural immunity to help prevent the initial damage from occurring. Alternatively, studies have shown that continuing to take vitamins after exposure to loud sounds can improve the quality of performance from the remaining, and otherwise undamaged cells, decreasing the overall hearing impairment.
Osteopenia
Not commonly known is a condition called Osteopenia in which the mineral density of bones decreases and can often be considered a precursor to osteoporosis.1 When Osteopenia affects the tiny bones within the ears, hearing loss can result. Often times this acquired form of hearing loss is attributed to age, when in fact the lack of certain nutrients is to blame. Taking the initiative to consume bone-strengthening vitamins like Vitamin D can ward off such deterioration and prevent the hearing loss from occurring.

Which Vitamins Help With Hearing Loss?
When intense sound vibrations caused by extremely loud noise reach the hair cells within the ear, the damage is caused by the release of free radicals into the bloodstream. The body releases these destructive molecules as a natural reaction to the intense noise exposure, and these molecules are the direct cause of the damage to the hair cells within the ear. By ingesting what are known as "Free Radical Scavengers" you can prevent these molecules from attacking the cells in the ear. Vitamin A, Vitamin E, and Lipoic Acid have all been used as successful Free Radical Scavengers and have shown to be effective at preventing noise-induced hearing loss.
Vitamin D, mentioned above, is a great nutritive source for increasing bone strength. Vital for the tiny bones within the ear, Vitamin D prevents the likelihood of deterioration and prolongs the effects of "age-related" hearing loss by keeping the organ strong. Studies show that Vitamin D deficiencies are continuously linked to sensorineural hearing loss.2 Avoiding Osteopenia is one way to prevent avoidable hearing damage.
Magnesium is another common nutrient used for hearing improvement, as it is known to increase blood flow within the ear. A common effect of the presence of free radicals is decreased blood flow, so to combat this, magnesium is usually used as an integral ingredient. The combination of Magnesium and other Vitamins can be a great start to improving ear health and remedying minor damage.
The Hearing Loss Pill
With the understanding that vitamins and nutrients can act as good sources of relief and protection against hearing loss, The Hearing Loss Pill takes this science one step further. The pill targets the nerves within the ear that are still functional and improves performance. This optimization provides protection and also targets the nerves within the brain to improve the process for which sound is registered. The Hearing Loss Pill not only optimizes the organ for receiving sound but also guards against the free radicals that can cause further damage. Included are other integral ingredients within the compound which are known to be essential for proper hearing function.
FAQ
Q: Are vitamins a cure for hearing loss?
A: No. Vitamins, and those contained within the Hearing Loss Pill, are used to strengthen immunity within the ear and optimize the undamaged cells.
Q: If I take vitamins before exposure to loud noise, do I still need to wear protection?
Yes! Ingesting vitamins, supplements, or the Hearing Loss Pill prior to extreme noise exposure should not act as a replacement for ear plugs or other forms of protection. While the dosage will help prevent extensive damage by increasing immunity and protecting against free radicals, ear plugs should still be warn to block intense sound.
Are you a good candidate for The Hearing Loss Pill? How much is a recommended dose? For these and other questions, refer to the full list of FAQs here.

